Latest updates Cisco CCNP Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOTv2) 300-135 exam questions and Answers! Free sharing 300-135 pdf online download, online exam Practice test, easy to improve skills! Get the full 300-135 exam dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html (Total questions:308 Q&A). Year-round updates! guarantee the first attempt to pass the exam!
[PDF] Free Cisco 300-135 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1t2DGWCrKH4lUzDTYYVUjacRNffholtDK
[PDF] Free Full Cisco pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1CMo2G21nPLf7ZmI-3_hBpr4GDKRQWrGx
300-135 TSHOOT – Cisco: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/exams/current-list/tshoot2.html#~stickynav=1
Latest effective Cisco 300-135 Exam Practice Tests
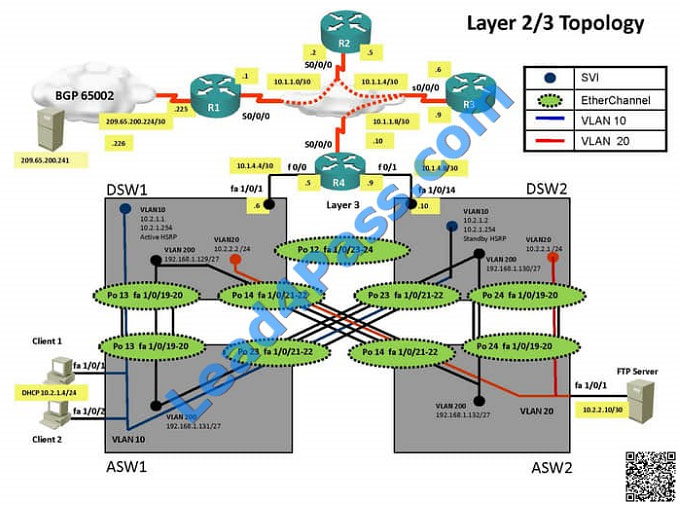
QUESTION 1
Which command will encrypt the enable password?
A. enable secret
B. service password-encryption
C. http://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
D. http://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 2
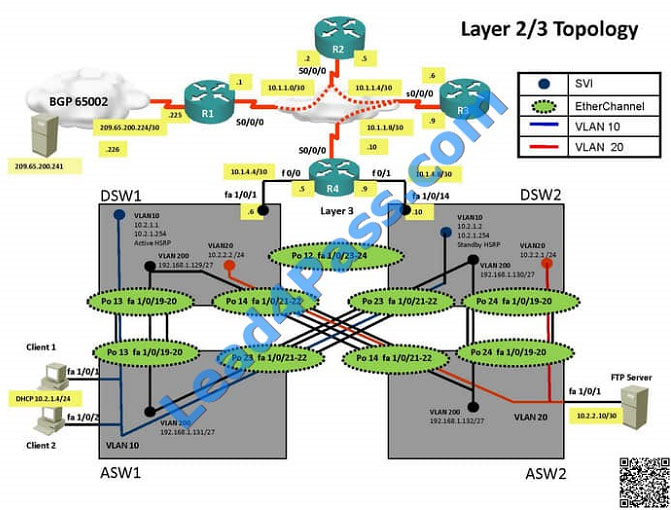
Refer to the topology.
SW1 Switch Management IP address is not pingable from SW4. What could be the issue?
A. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk links between SW1 and SW4
B. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk links between SW1 and SW2
C. Management VLAN not allowed in the trunk link between SW2 and SW4
D. Management VLAN ip address on SW4 is configured in wrong subnet
E. Management VLAN interface is shutdown on SW4
Correct Answer: D
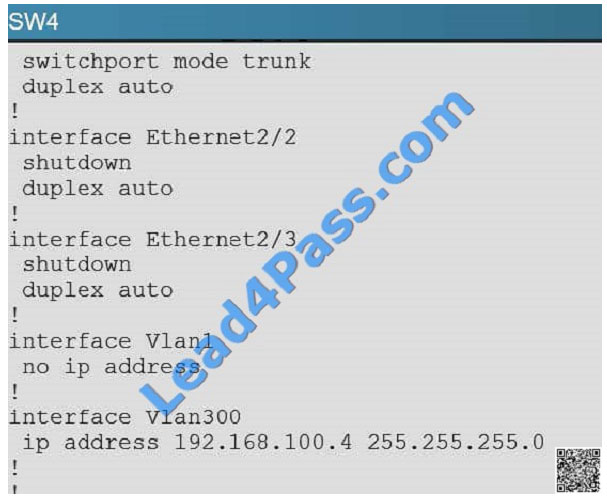
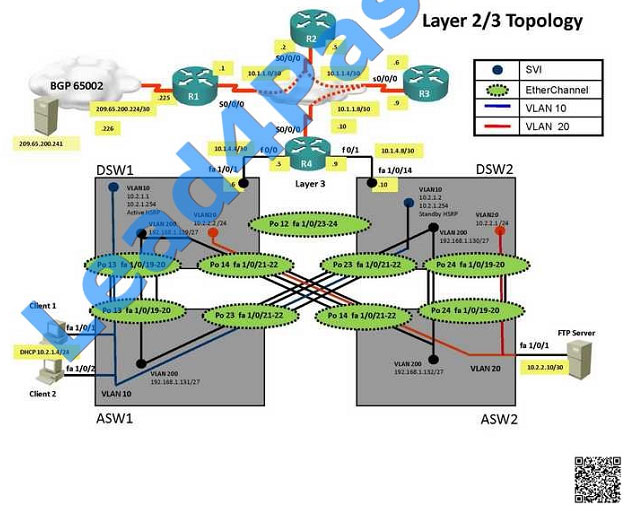
In the network, VLAN 300 is called the Management VLAN. Based on the configurations shown below, SW1 has VLAN
300 configured with the IP address of 192.168.10.1/24, while on SW4 VLAN 300 has an IP address of
192.168.100.4/24, which is not in the same subnet.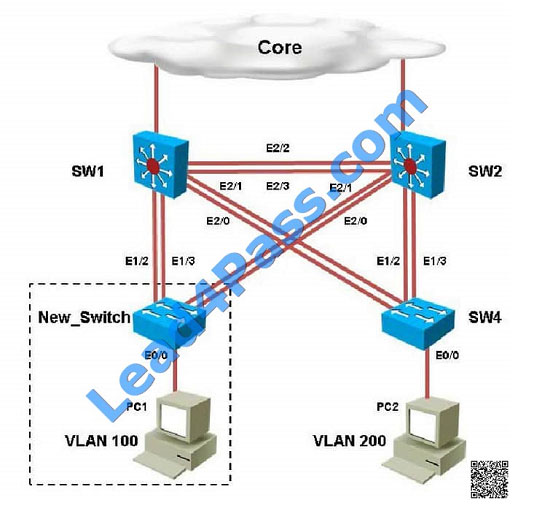
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You
have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems. 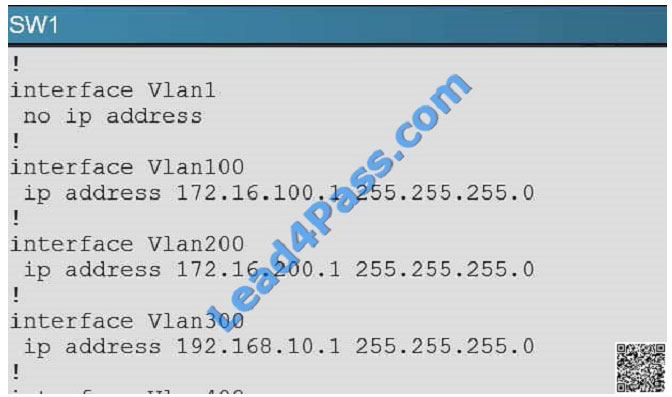
QUESTION 3
Which of the following are byproducts of a structured maintenance plan? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Predictable security vulnerabilities
B. Economies of scale
C. Improved expenditure forecasts
D. Increased downtime
E. Predictable equipment obsolescence
F. Consumption of fewer resources
Correct Answer: ABCEF
QUESTION 4
How do you make sure AAA will still allow you to login if TACACS+ fails? (Choose two.)
A. aaa authentication login test group local tacacs+
B. aaa authentication login test group tacacs+ local
C. aaa authentication login test group radius local
D. aaa authentication ppp dialins group tacacs+ local
E. https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: BD
QUESTION 5
===============================================================================
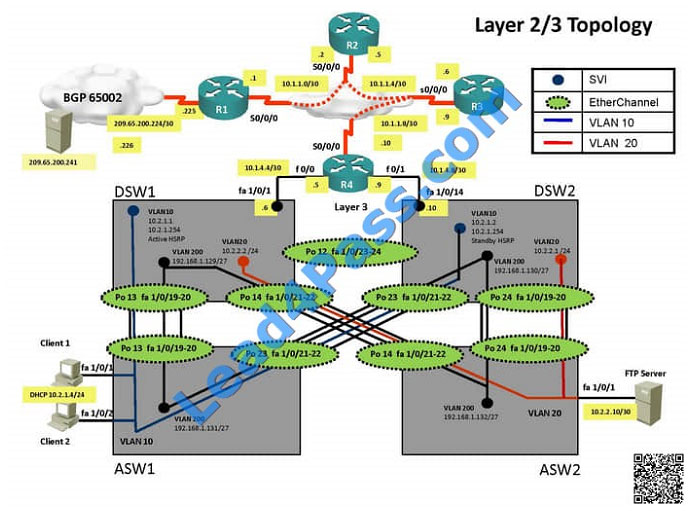 Solution
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
Since the problem is raised that DSW1 will not become active router for HSRP group 10
we will check for the HSRP configuration…
DSW1 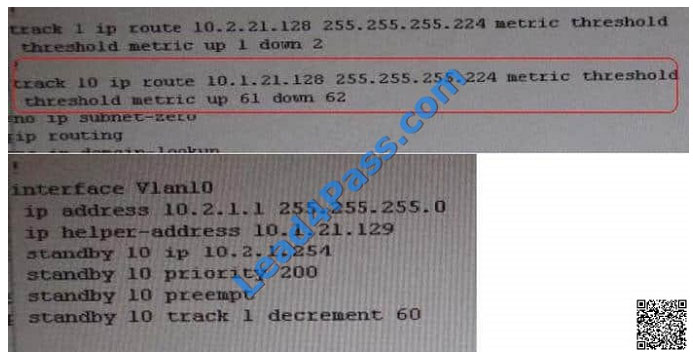 DSW2
DSW2
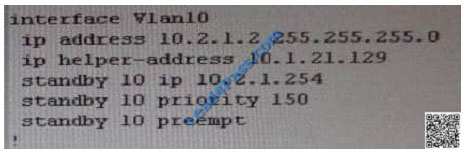
From snapshot we see that the track command given needs to be changed under active VLAN10 router
Change Required: On DSW1, related to HSRP, under vlan 10 change the given track 1 command to instead use the
track 10 command.
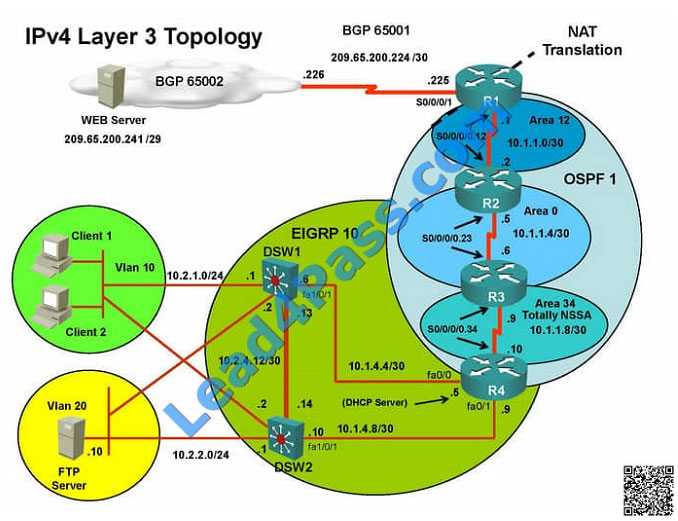
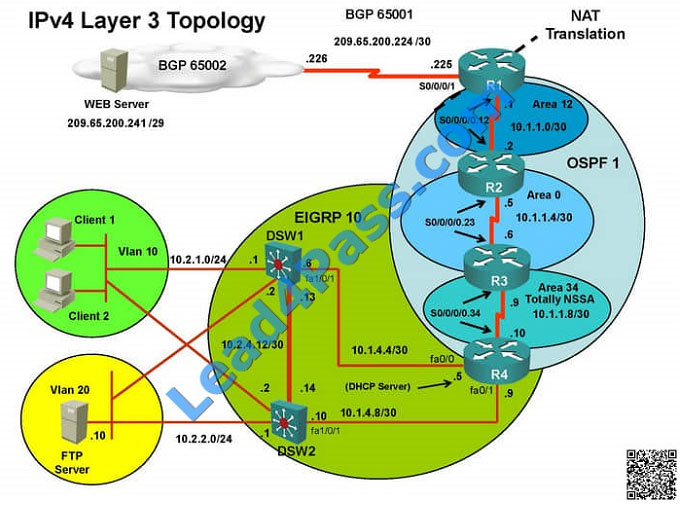
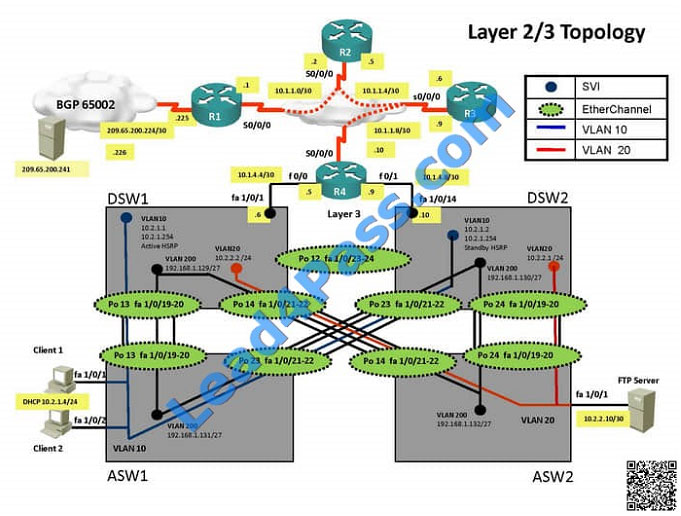
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened DSW1 will not become the active router for
HSRP
group 10.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
A. R1
B. R2
C. R3
D. R4
E. DSW1
F. DSW2
G. ASW1
H. ASW2
Correct Answer: E
DSW references the wrong track ID number.
In this case we know that the problem is with HSRP and that DSW1 will not become the active router. Since we know
that HSRP communication is working between DSW1 and DSW2, we can deduce that the problem must be with
DSW1.
QUESTION 6
How to check MTU of interface using ping? / How can you check the links mtu size with ping command?
A. ping 10.1.1.1 size 1501
B. ping 10.1.1.1 size 1500 df-bit
C. ping 10.1.1.1
D. ping 10.1.1.1 no-size
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 7
Which of the following statements regarding documentation would not be considered a helpful step in the
troubleshooting process?
A. Use the Cisco Auto Configuration tool.
B. Use the Cisco Rollback feature.
C. Automate documentation.
D. Schedule documentation checks.
E. Use the Cisco Configuration Archive tool.
F. Require documentation prior to a ticket being closed out.
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 8
Drag and Drop – Configuring SSH Sequence
Drag and drop the sequence for configuring SSH in the correct order onto the right.
Select and Place: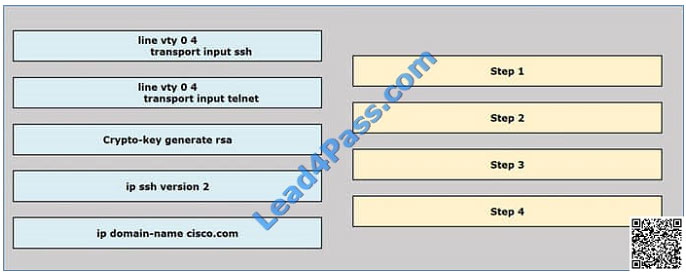 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer: 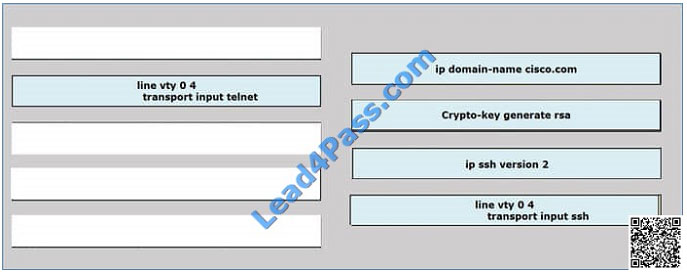
QUESTION 9
A question related to Cisco password security.
A. Enable secret is strong than enable password with 7.
B. Weaker revisable algorithms that are hashed and encrypted related (with 5 and 7).
C. https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 10
A user is able to log into the switch but cannot enable . What might be the reason
A. change authorization level
B. change accounting
C. change authentication
D. https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 11
Which IPsec mode with least overhead?
(A question about IPsec mode encrypted with least overhead.)
A. transport
B. dynamic
C. transparent
D. tunnel
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 12
Which of the statements are true regarding traceroute?
A. Default DF bit is set to 0.
B. Includes additional header option like verbose
C. Default it try 3 times for each hop count.
D. https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 13
A new router is added to an existing HSRP standby group. One of the existing routers is in an active state, the other is
in a standby state. Under what circumstance will the new router become the active router?
A. The new router will become active immediately because it\\’s the newest router introduced into the group.
B. The new router can become active only when the existing active router and the existing standby router become
unavailable.
C. The new router has a lower priority value.
D. The new router will never become active unless the existing active router becomes unavailable.
E. The new router has preempt configured and a higher priority
F. The new router has a higher priority value.
Correct Answer: E
QUESTION 14
Based on the network diagram, this link should be added to Area 1, not Area 2.
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing
network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.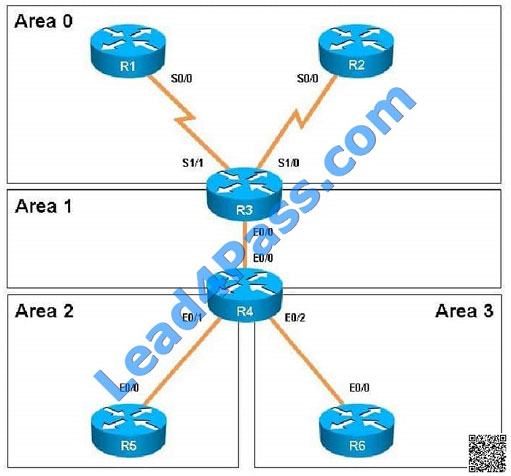
The 6.6.0.0 subnets are not reachable from R4. how should the problem be resolved?
A. Edit access-list 46 in R6 to permit all the 6.6.0.0 subnets
B. Apply access-list 46 in R6 to a different interface
C. Apply access-list 1 as a distribute-list out under router ospf 100 in R4
D. Remove distribute-list 64 out on R6
E. Remove distribute-list 1 in ethernet 0/1 in R4
F. Remove distribute-list 1 in ethernet 0/0 in R4
Correct Answer: D
Here we see from the running configuration of R6 that distribute list 64 is being used in the outbound direction to all OSPF neighbors. 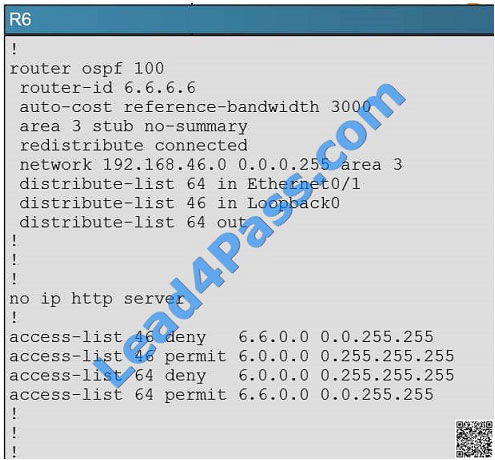
QUESTION 15
Scenario:
You have been asked by your customer to help resolve issues in their routed network. Their network engineer has
deployed HSRP. On closer inspection HSRP doesn\\’t appear to be operating properly and it appears there are other
network
problems as well. You are to provide solutions to all the network problems. Examine the configuration on R5. Router R5
do not see any route entries learned from R4; what could be the issue?
A. HSRP issue between R5 and R4
B. There is an OSPF issue between R5 and R4
C. There is a DHCP issue between R5 and R4
D. The distribute-list configured on R5 is blocking route entries
E. The ACL configured on R5 is blocking traffic for the subnets advertised from R4.
Correct Answer: C
R5 configuration :int gig0/0 ip address dhcp This interface not getting dhcp ip address from R4. So even though OSPF
configuration was like 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0 , because this interface does not get correct ip address from DHCP it can’t
participate in OSPF. R4 configuration :ip dhcp exlude address ip dhcp pool ine network x.x.x.x x.x.x.x i think default
router command was missing here . not sure but Int gig0/0 ip address dhcp . This interface on R4 should have ip
address configured on it instead of ” ip address dhcp ” . Hence its not able to provide dhcp lease address to R5. R4
also had ospf configured as network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0. So all interface can participate if they are up and if they have
ip address. But because R5 interface connected to R4 could not obtail correct dhcp ip address from R4 due to DHCP
issue they wont form ospf neighborship. So correct answer is DHCP issue between R5 and R4.
QUESTION 16
===============================================================================
 Solution
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
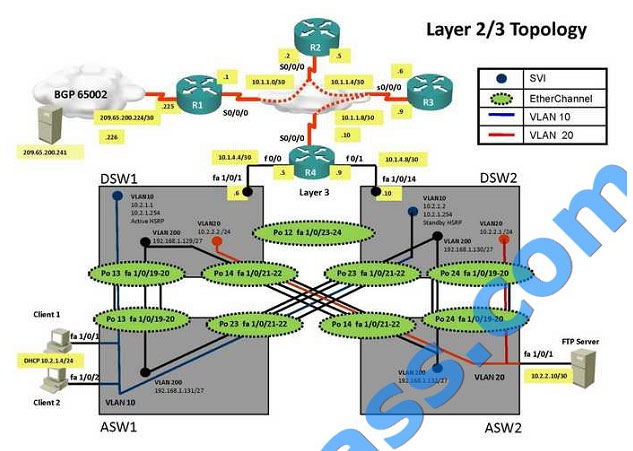
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig —– Client will be
receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
From Client PC we can ping 10.2.1.254….
But IP 10.2.1.3 is able to ping from R4, R3, R2, R1.
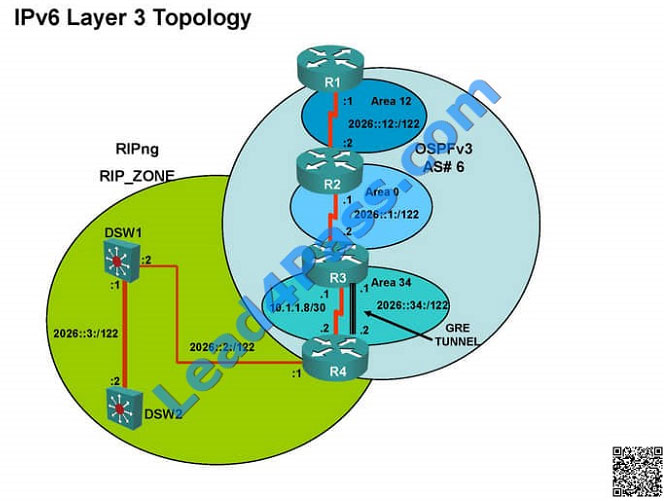
Since the problem is R1 (2026::111:1) is not able to ping loopback of DSW1 (2026::102:1).
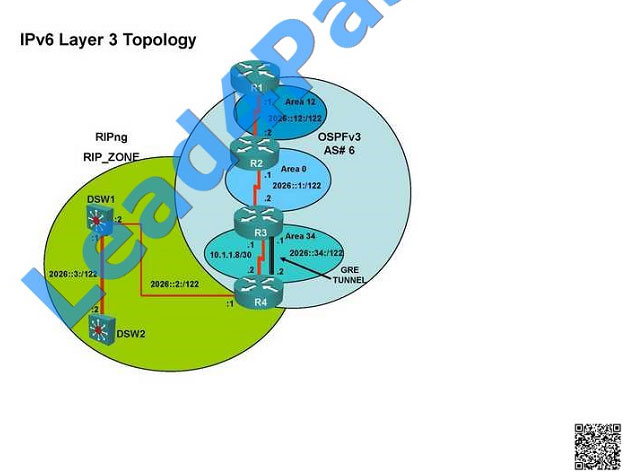
Kindly check for neighbourship of routers as IPV6…. As per design below neighbourship should be present for IPV6 R1
—R2 — R3 — R4— DSW1 and DSW2 —– Neighbourship between devices of IPV6
As per above snapshot we cannot see IPV6 neighbourship between R2 and R3 when checked interface configuration
ipv6 ospf area 0 is missing on R2 which is connected to R3
Change required: On R2, IPV6 OSPF routing, Configuration is required to add ipv6 ospf 6 area 0 under interface serial
0/0/0.23  R2 IPV6 OSPF neighbourship is with R1 R3 IPV6 OSPF neighbourship is with R4
R2 IPV6 OSPF neighbourship is with R1 R3 IPV6 OSPF neighbourship is with R4
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing schemes, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that the
loopback address on R1 (2026::111:1) is not able to ping the loopback address on DSW2(2026::102:1).
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
A. R1
B. R2
C. R3
D. R4
E. DSW1
F. DSW2
G. ASW1
H. ASW2
Correct Answer: B
R2 is missing the needed IPV6 OSPF for interface s0/0/0.23.
Since both DSW1 and R4 cannot ping R2\\’s loopback or R2\\’s s0/0/0/0.12 interface we should start by examining the
configuration of R2. R2 is also not an IPv3 neighbor of R3. If you look at the configuration of R2 you will notice that
OSPFv3
has not been enabled on the connection to R3, confirming that the fault condition is on R2.
QUESTION 17
===============================================================================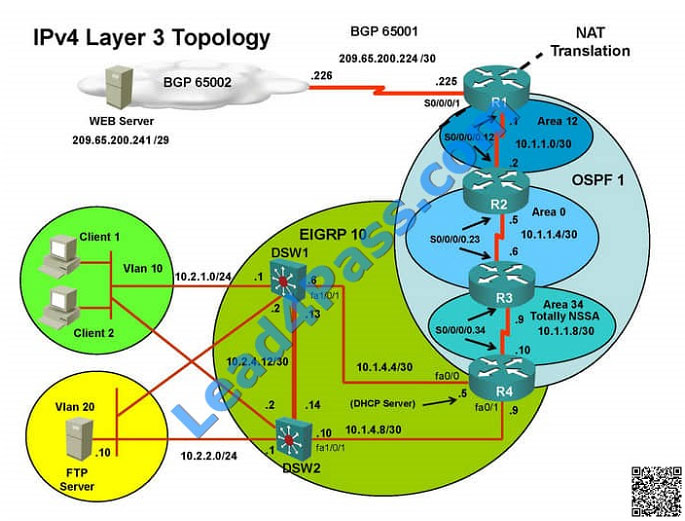
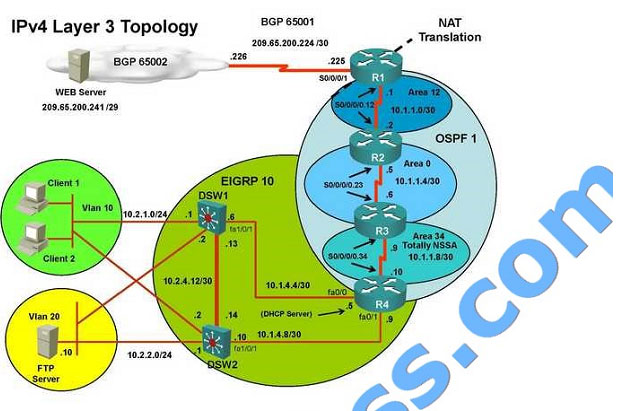
 Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 Ipconfig —– Client will be
receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– State of BGP will be in established state and will be able to receive I prefix (209.65.200.241)
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 and BGP is also receiving prefix of webserver and we
are able to ping the same from R1. Further troubleshooting needs to be done on R1 on serial 0/0/1
Check for running config. i.e sh run for interface serial 0/0/1..
From above snapshot we are able to see that IP needs to be PAT to serial 0/0/1 to reach web server IP
(209.65.200.241). But in access-list of NAT IP allowed IP is 10.1.0.0/16 is allowed and need 10.2.0.0 /16 to
As per troubleshooting we are able to ping ip 10.2.1.3 from R1 and BGP is also receiving prefix of web server and we
are able to ping the same from R1. Its should be checked further for running config of interface for stopping
Change required: On R1 we need to add the client IP address for reachability to server to the access list that is used to
specify which hosts get NATed.
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 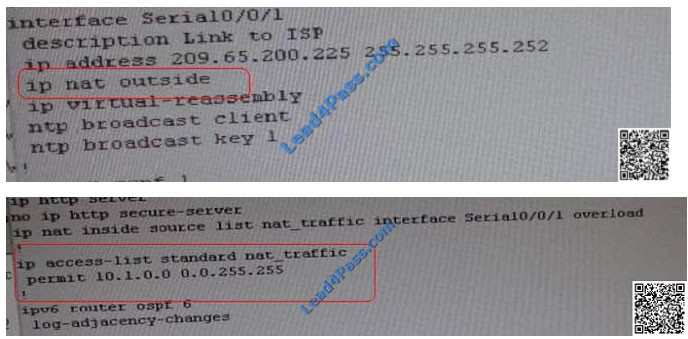 209.65.200.241 address.
209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
The fault condition is related to which technology?
A. BGP
B. NTP
C. IP NAT
D. IPv4 OSPF Routing
E. IPv4 OSPF Redistribution
F. IPv6 OSPF Routing
G. IPv4 layer 3 security
Correct Answer: C
On R1 we need to add the client IP address for reachability to server to the access list that is used to specify which
hosts get NATed.
Clients 1 and 2 belong in the 10.2.0.0 subnet, as if you observe the NAT configuration you will notice that only 10.1.0.0
are specified in the NAT pool. Clients 1 and 2 are not being translated when they should be. The problem is with the
NAT
configuration on R1.
QUESTION 18
Which of the following are common issues that should be considered when establishing or troubleshooting site-to-site
VPNs? (Choose all that apply.)
A. User authentication
B. Overlapping IP address space
C. GRE or IPsec configuration
D. MTU size
E. VPN client software
F. Authentication server configured ly
Correct Answer: BCD
QUESTION 19
You have been brought in to troubleshoot an EIGRP network. A network engineer has made configuration changes to
the network rendering some locations unreachable. You are to locate the problem and suggest solution to resolve the
issue.
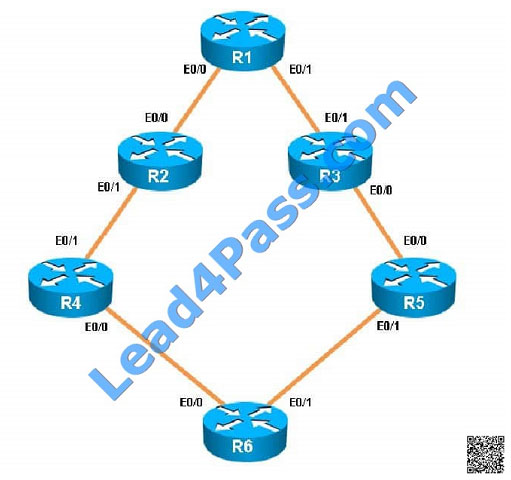 R5 has become partially isolated from the remainder of the network. R5 can reach devices on directly connected
R5 has become partially isolated from the remainder of the network. R5 can reach devices on directly connected
networks but nothing else. What is causing the problem?
A. An outbound distribute list in R3
B. Inbound distribute lists in R5
C. An outbound distribute list in R6
D. Incorrect EIGRP routing process ID in R5
Correct Answer: B
Here we see that distribute list 3 has been applied to EIGRP on router R%, but access-list 3 contains only deny
statements so this will effectively block all routing advertisements from its two EIGRP neighbors, thus isolating R5 from
the rest of the EIGRP network: 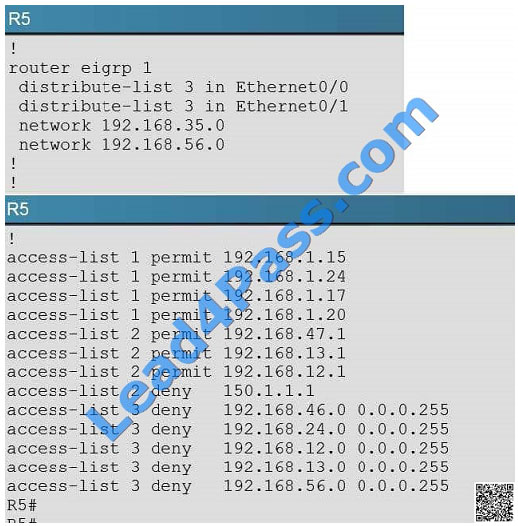
QUESTION 20
Refer to the exhibit. How would you confirm on R1 that load balancing is actually occurring on the default- network
(0.0.0.0)?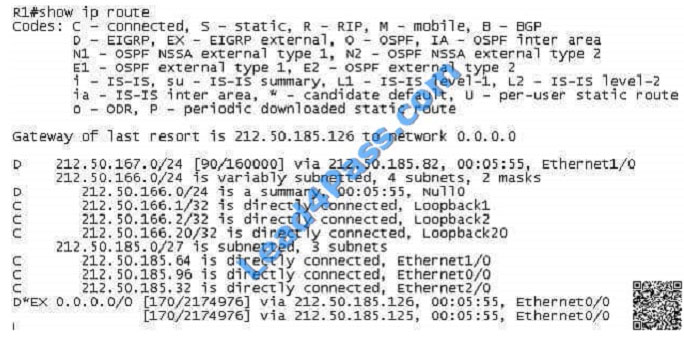 A. Use ping and the show ip route command to confirm the timers for each default network resets to 0.
A. Use ping and the show ip route command to confirm the timers for each default network resets to 0.
B. Load balancing does not occur over default networks; the second route will only be used for failover.
C. Use an extended ping along with repeated show ip route commands to confirm the gateway of last resort address
toggles back and forth.
D. Use the traceroute command to an address that is not explicitly in the routing table.
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 21
===============================================================================
 Client 1 is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Client 1 is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig —– Client will be
receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
From Client PC we can ping 10.2.1.254….
But IP 10.2.1.3 is not able to ping from R4, R3, R2, R1
Change required: On DSW1, VALN ACL, Need to delete the VLAN access-map test1 whose action is to drop access-list
10; specifically 10.2.1.3 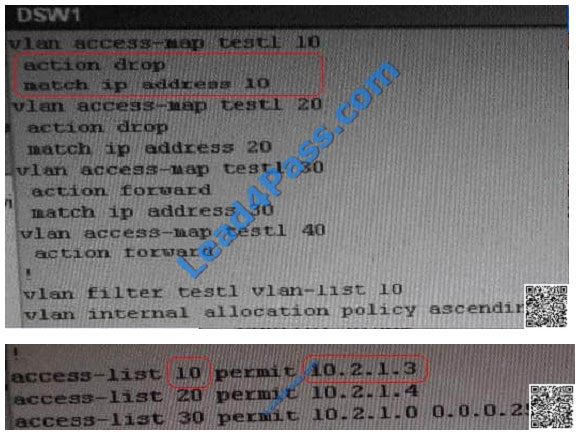 The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble
ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
The fault condition is related to which technology?
A. NTP
B. IP DHCP Helper
C. IPv4 EIGRP Routing
D. IPv6 RIP Routing
E. IPv4 layer 3 security
F. Switch-to-Switch Connectivity
G. Loop Prevention
H. Access Vlans
I. Port Security
J. VLAN ACL / Port ACL
K. Switch Virtual Interface
Correct Answer: J
On DSW1, VALN ACL, Need to delete the VLAN access-map test1 whose action is to drop access-list 10; specifically
10.2.1.3 Since Client1 is not able to ping DSW1 we can deduce that the problem lies with DSW1. Upon closer
examination we see that the VLAN filter list being applied to this device is filtering out the network that DSW is on. So
the problem is VLAN Access Map.
QUESTION 22
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct?(chose two)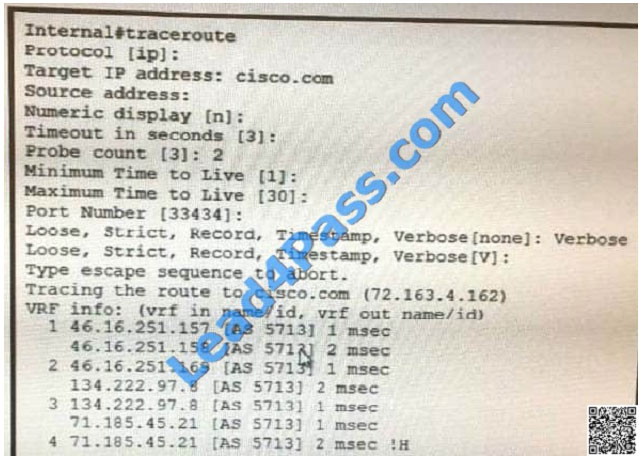 A. The source device has name resolution configured
A. The source device has name resolution configured
B. The source is using two routes for the destination,learned from different protocols
C. A device on the path is introducing considerable delay
D. The source device is load balancing traffic
Correct Answer: AD
Router traces domain name (cisco.com) and it gets ICMP answers, so name resolution has happened. Per hop output
shows 2 lines, hence 2 active paths exist.
QUESTION 23
You are troubleshooting an issue with a GRE tunnel between R1 and R2 and find that routing is OK on all intermediary
routers.
The tunnel is up on R1, but down on R2.
Which two possible issues can prevent the tunnel from coming up? (Choose two)
A. the tunnel dose not come up unless traffic is sent through it
B. the tunnel source interface is down on R2
C. No specific route to the tunnel destination is on R2; only a default route.
D. R2 dose not know how to reach the tunnel destination
E. The tunnel keepalive timer does not match on R1 and R2
Correct Answer: BD
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/generic-routing-encapsulation-gre/118361-technotegre-00.html
QUESTION 24
Several troubleshooters are about to work on the same problem. Which of the following troubleshooting methods would
be most appropriate to make the best use of the troubleshooters1 time?
A. Bottom up
B. Component swapping
C. Top down
D. Shoot from the hip
E. Divide and conquer
F. Follow the traffic path
Correct Answer: E
QUESTION 25
===============================================================================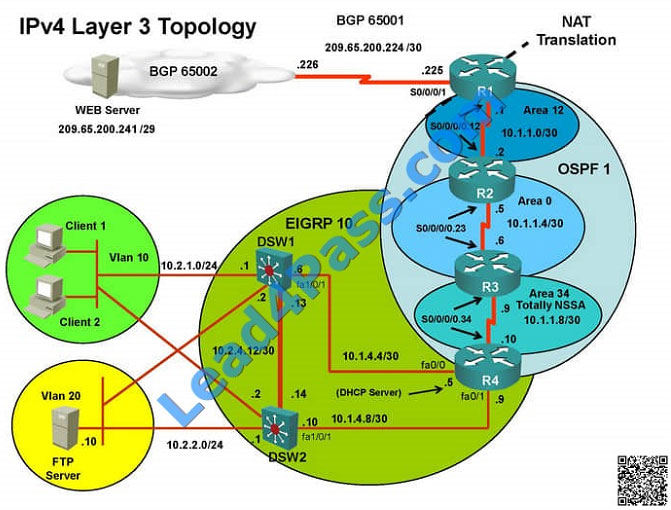
 Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241…
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241…
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4
Ipconfig —– Client will be receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2, R1
Look for BGP Neighbourship
Sh ip bgp summary —– State of BGP will be in active state. This means connectivity issue between serial
Check for running config. i.e sh run — over here check for access-list configured on interface as BGP is down (No need
to check for NAT configuration as its configuration should be right as first need to bring BGP up)
In above snapshot we can see that access-list of edge_security on R1 is not allowing wan IP network
Change required: On R1, we need to permit IP 209.65.200.222/30 under the access list 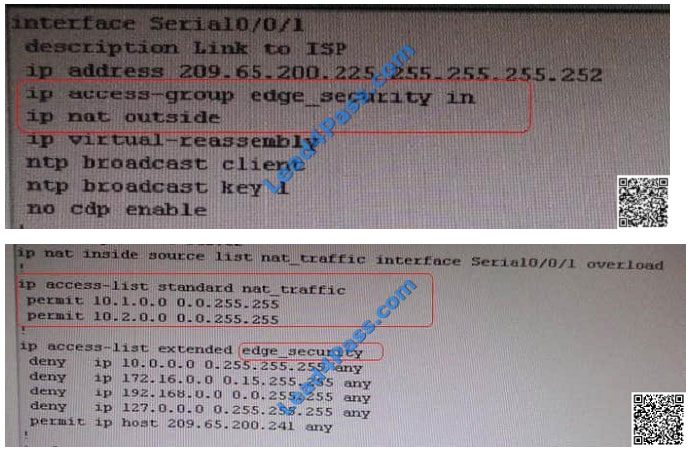 The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the
209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
A. Under the interface Serial0/0/1 enter the ip access-group edge_security out command.
B. Under the ip access-list extended edge_security configuration add the permit ip 209.65.200.224 0.0.0.3 any
command.
C. Under the ip access-list extended edge_security configuration delete the deny ip 10.0.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 any
command.
D. Under the interface Serial0/0/0 configuration delete the ip access-group edge_security in command and enter the ip
access-group edge_security out command.
Correct Answer: B
On R1, we need to permit IP 209.65.200.222/30 under the access list.
Based on the configuration shown, we can see that only the web server is allowed access on R1 according to the
access list. BGP uses TCP port 179 to establish a peering relationship, and we can see that the BGP routers that needs
to peer
with R1 is not allowed to do so, so they are not able to exchange routes. By allowing all IP packets from the
209.65.200.224/30 network, BGP would be established and connectivity would be restored.
QUESTION 26
Which command will limit debug output ppp authentication on serial 0/1 and serial 0/2?
A. debug condition interface range s0/1 -0/2 debug ppp authentication
B. debug condition interface s0/1 and 0/2 debug ppp authentication
C. debug int s0/1 debug int 0/2 debug ppp authentication
D. Debug condition interface s0/1 Debug condition interface s0/2 debug ppp authentication
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 27
===============================================================================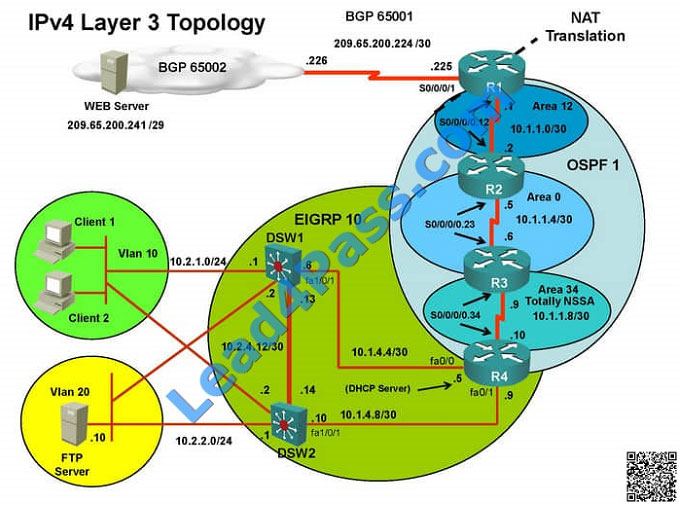
 Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 Ipconfig —– Client will be
receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , R3, R2 but not from R1
Check for neighborship of ospf sh ip ospf nei —– Only one neighborship is forming with R2 and i.e. with R3 Since R2 is
connected to R1 and R3 with routing protocol ospf than there should be 2 neighbors seen but only one is seen
Need to check running config of R2 and R3 for interface Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0.12 on R2
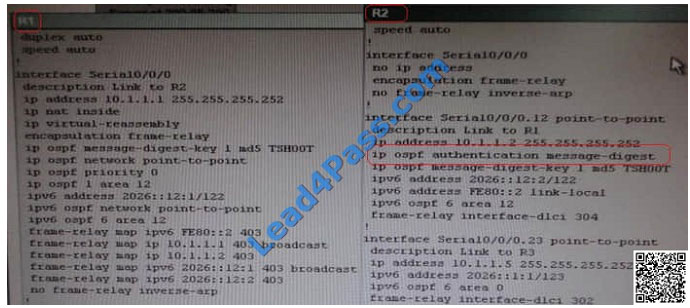 Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0 on R1 Change required: On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF
Sh run ————————– Interface Serial0/0/0/0 on R1 Change required: On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF
command is missing and required to configure—— ip ospf authentication message-digest
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the
209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
A. Enable OSPF authentication on the s0/0/0 interface using the ip ospf authentication message-digest command
B. Enable OSPF routing on the s0/0/0 interface using the network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 12 command.
C. Enable OSPF routing on the s0/0/0 interface using the network 209.65.200.0 0.0.0.255 area 12 command.
D. Redistribute the BGP route into OSPF using the redistribute BGP 65001 subnet command.
Correct Answer: A
On R1, for IPV4 authentication of OSPF the command is missing and required to configure—— ip ospf authentication
message-digest R2 is correctly configured for OSPF authentication, including the “ip ospf authentication message-
digest” command listed properly under the sub-interface Serial0/0/0.12. R1 is missing this command
QUESTION 28
Scenario:
A customer network engineer has edited their OSPF network configuration and now your customer is experiencing
network issues. They have contacted you to resolve the issues and return the network to full functionality.
Connectivity from R3 to R4, R5 and R6 has been lost. How should connectivity be reestablished?
A. Configure R4 with a virtual link to 192.168.13.2
B. Change the R3 and R4 hello-interval and retransmit-interface timers to zero so the link won\\’t go down.
C. Add an OSPF network statement for 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 1 in R3
D. Add an OSPF network statement for 192.168.34.3 0.0.0.255 area 2 in R3
E. Add an OSPF network statement for 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 1 in R3
Correct Answer: E
Based on the network diagram, we know that a virtual link will need to be configured to logically connect area 2 to the
back area 0. However, this is not the problem as we can see that R3 has been correctly configured to do this. It is,
however, missing the network statement for the link to R4. Here, we see that the link to R4 is using the 192.168.34.0
network, but that this network has not been added to OSPF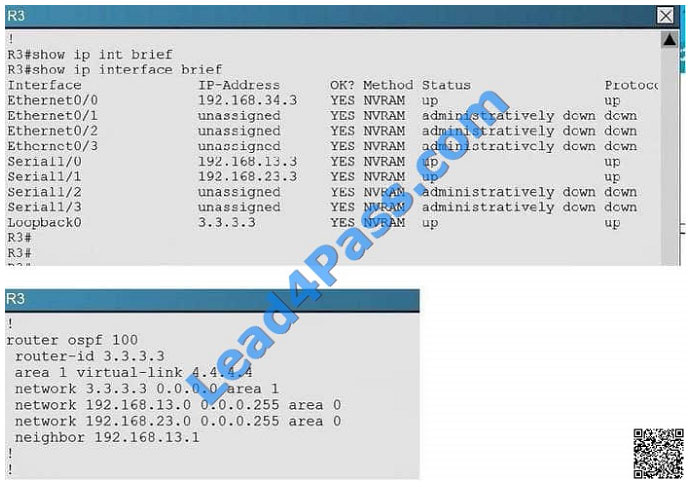 Based on the network diagram, this link should be added to Area 1, not Area 2.
Based on the network diagram, this link should be added to Area 1, not Area 2.
QUESTION 29
The loop guard feature makes additional checks. If BPDUs are not received on a nondesignated port, and loop guard is
enabled, that port is moved into the STP loopinconsistent blocking state, instead of the listening / learning / forwarding
state. Without the loop guard feature, the port assumes the designated port role. The port moves to the STP forwarding
state and creates a loop.
A customer network engineer has made configuration changes that have resulted in some loss of connectivity. You
have been called in to evaluate a switch network and suggest resolutions to the problems.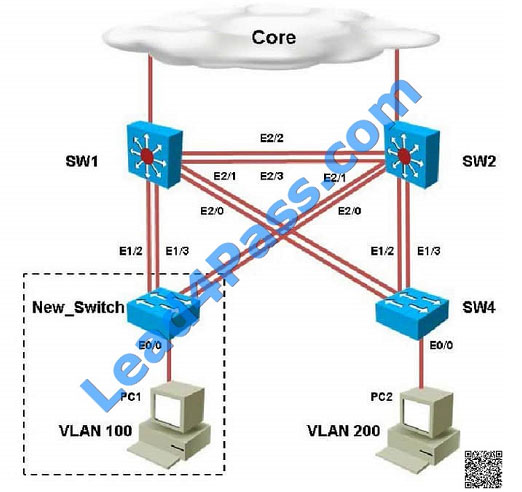
PC2 in VLAN 200 is unable to ping the gateway address 172.16.200.1; identify the issue.
A. VTP domain name mismatch on SW4
B. VLAN 200 not configured on SW1
C. VLAN 200 not configured on SW2
D. VLAN 200 not configured on SW4
Correct Answer: D
By looking at the configuration for SW2, we see that it is missing VLAN 200, and the “switchport access vlan 200”
command is missing under interface eth 0/0: 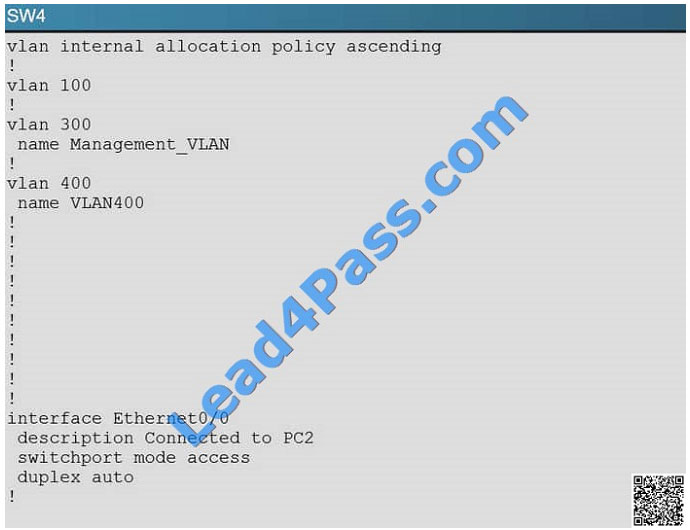
QUESTION 30
Which command enables authenticated login if a TACACS+ failure occurs?
A. aaa authentication login test group local tacacs+
B. aaa authentication login test group tacacs+ local
C. aaa authentication login test group radius local
D. aaa authentication ppp dialins group tacacs+ local
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 31
===============================================================================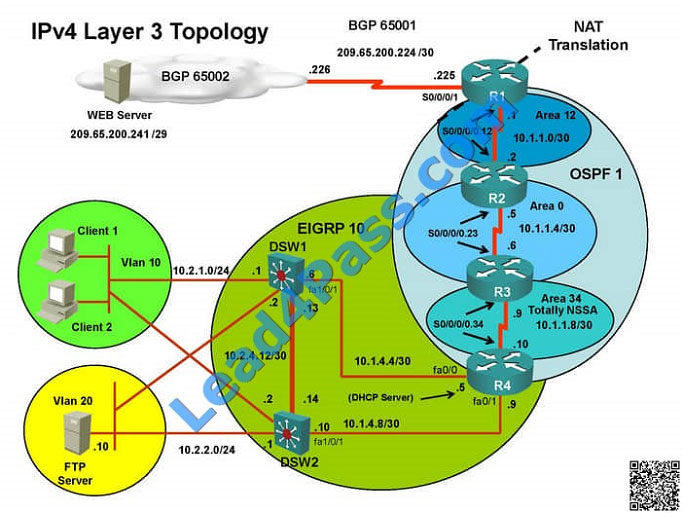
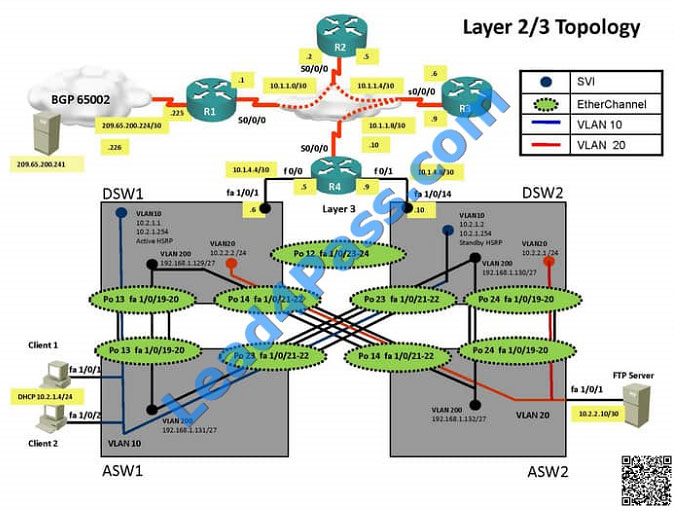 Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:
When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address from R4 ipconfig —– Client will be
receiving IP address 10.2.1.3
IP 10.2.1.3 will be able to ping from R4 , but cannot ping from R3, R2, R1
This clearly shows problem at R4 since EIGRP is between DSW1, DSW2 and R4 and OSPF protocol is running
between R4, R3, R2, R1 so routes from R4 are not propagated to R3, R2, R1
Since R4 is able to ping 10.2.1.3 it means that routes are received in EIGRP and same needs to be advertised in OSPF
to ping from R3, R2, R1.
Need to check the routes are being advertised properly or not in OSPF and EIGRP vice-versa.
From above snap shot it clearly indicates that redistribution done in EIGRP is having problem and by default all routes
are denied from ospf to EIGRP… so need to change route-map name.
Change required: On R4, in the redistribution of EIGRP routing protocol, we need to change name of route-map to
resolve the issue. It references route-map OSPF_to_EIGRP but the actual route map is called OSPF->EIGRP 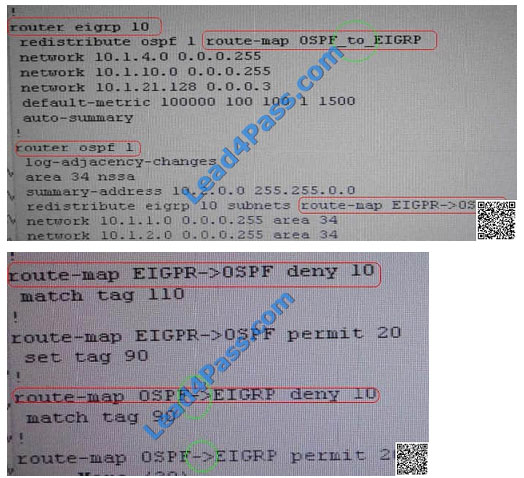
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, layer 2 connectivity,
FHRP services, and device security, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the
209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
On which device is the fault condition located?
A. R1
B. R2
C. R3
D. R4
E. DSW1
F. DSW2
G. ASW1
H. ASW2
Correct Answer: D
On R4, in the redistribution of EIGRP routing protocol, we need to change name of routemap to resolve the issue. It
references route-map OSPF_to_EIGRP but the actual route map is called OSPF->EIGRP. Since Client 1 is able to ping
the near-end interface of the router R4 but not the far-end interface, we can be reasonably certain that the fault
condition is with R4.
QUESTION 32
You have the followings commands on your Cisco Router:
ip ftp username admin ip ftp password backup
You have been asked to switch from FTP to HTTP. Which two commands will you use to replace the existing
commands?
A. ip http username admin
B. ip http client username admin
C. ip http password backup
D. ip http client password backup
E. ip http server username admin
F. ip http server password backup
Correct Answer: BD
Configuring the HTTP Client Perform this task to enable the HTTP client and configure optional client characteristics.
The standard HTTP 1.1 client and the secure HTTP client are always enabled. No commands exist to disable the HTTP
client. For information about configuring optional characteristics for the HTTPS client, see the HTTPS-HTTP Server and
Client with SSL 3.0, Release 12.2(15)T, feature module.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ip http client cache {ager interval minutes | memory {file file- size-limit | pool pool-size-limit}
4.
ip http client connection {forceclose | idle timeout seconds | retry count | timeout seconds}
5.
ip http client password password
6.
ip http client proxy-server proxy-name proxy-port port-number
7.
ip http client response timeout seconds
8.
ip http client source-interface type number
9.
ip http client username username
Reference: HTTP 1.1 Web Server and Client.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/netmgmt/configuration/guide/nm_http_web.html
QUESTION 33
Which of the following is an unlikely reason for the ARP process to fail?
A. CEF switching is disabled on the switch
B. The source device and destination device are in different VLANs
C. The VLAN is excluded from the trunk
D. The host is connected to the switch through an IP phone
E. A faulty cable from host to switch or between switches
F. The trunking encapsulation type is inconsistent on the two ends of the link
Correct Answer: AD
QUESTION 34
What IP header option fields can you modify in an extended ping? (Choose three.)
A. Value
B. Strict
C. Record
D. Timestamp
E. Timeout
Correct Answer: BCD
QUESTION 35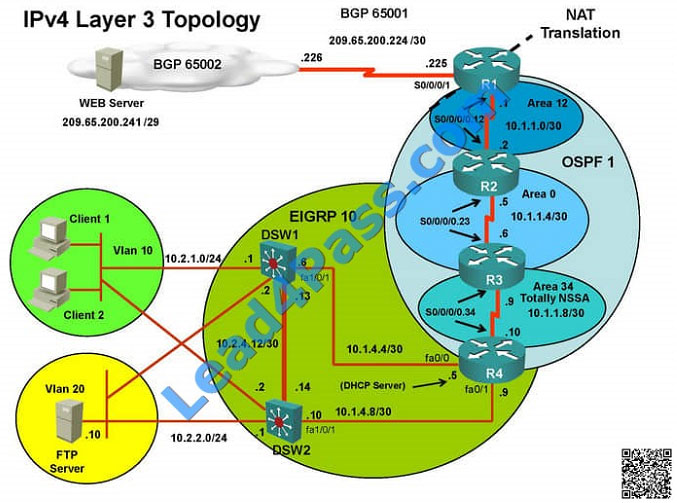
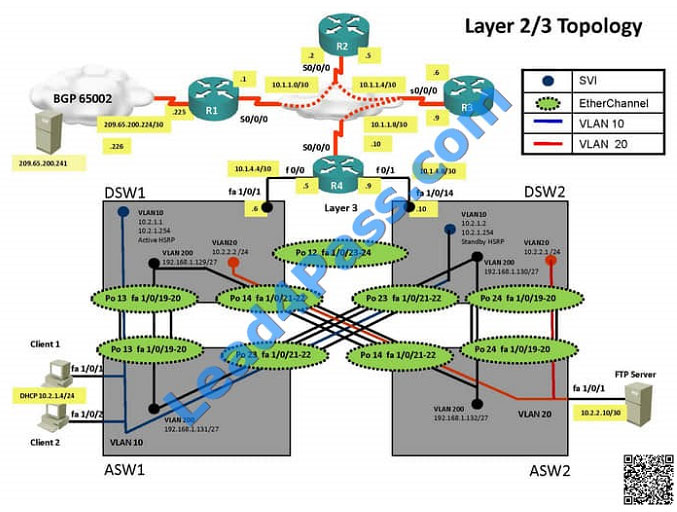
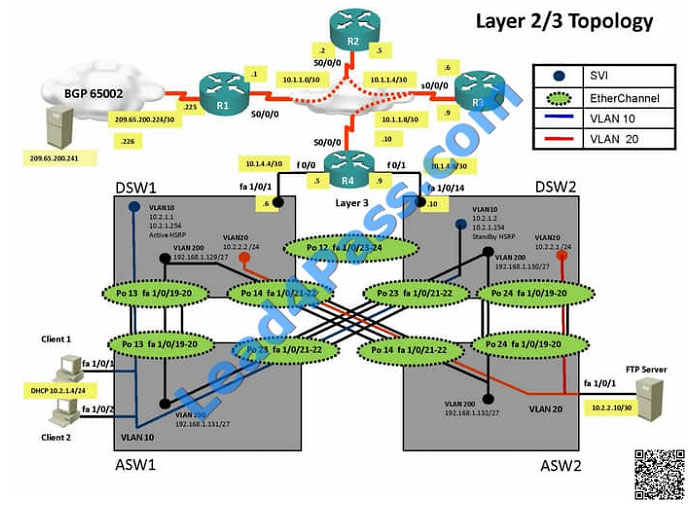 Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Client is unable to ping IP 209.65.200.241
Solution
Steps need to follow as below:When we check on client 1 and Client 2 desktop we are not receiving DHCP address
from R4 Ipconfig —– Client will be getting 169.X.X.X
On ASW1 port Fa1/0/ 1 and Fa1/0/2 access port VLAN 10 was assigned which is using IP address 10.2.1.0/24 Sh run
——- and check for running config of int fa1/0/1 and fa1/0/2
==================================================== interface FastEthernet1/0/1switchport mode
accessswitchport access vlan 10interface FastEthernet1/0/2switchport mode accessswitchport access vlan 10
====================================================
We need to check on ASW 1 trunk port the trunk Po13 and Po23 were receiving VLAN 20 and 200 but not VLAN 10 so
that switch could not get DHCP IP address and was failing to reach IP address of Internet
Change required: On ASW1 below change is required for switch-to-switch connectivity..
int range portchannel13,portchannel23 switchport trunk allowed vlan none switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,200 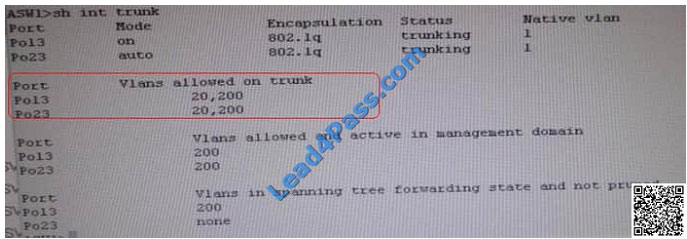 The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
The implementations group has been using the test bed to do a ‘proof-of-concept’ that requires both Client 1 and Client
2 to access the WEB Server at 209.65.200.241.
After several changes to the network addressing, routing scheme, DHCP services, NTP services, and FHRP services, a
trouble ticket has been opened indicating that Client 1 cannot ping the 209.65.200.241 address.
Use the supported commands to isolated the cause of this fault and answer the following questions.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
A. In Configuration mode, using the interface port-channel 13 command, then configure switchport trunk allowed vlan
none followed by switchport trunk allowed vlan 20,200 commands.
B. In Configuration mode, using the interface port-channel 13, port-channel 23, then configure switchport trunk none
allowed vlan none followed by switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,200 commands.
C. In Configuration mode, using the interface port-channel 23 command, then configure switchport trunk allowed vlan
none followed by switchport trunk allowed vlan 20,200 commands.
D. In Configuration mode, using the interface port-channel 23, port-channel, then configure switchport trunk allowed vlan
none followed by switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,200 commands.
Correct Answer: B
We need to allow VLANs 10 and 200 on the trunks to restore full connectivity. This can be accomplished by issuing the
“switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,200” command on the port channels used as trunks in DSW1.
QUESTION 36
Which two requirements are used for GRE? (Choose two.)
A. Protocol 47 should be allowed.
B. Destination of the tunnel should be reachable.
C. http://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
D. http://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html
Correct Answer: AB
QUESTION 37
A question about which login procedure will ask first. You see a running config user logins. aaa new-model aaa
authentication login default tacacs+ enable aaa authentication login ONLYLOCAL local aaa authentcation ppp default
radius local username Cisco password Cisco123 line vty 0 4
A. local
B. line
C. RADIUS
D. TACACS+
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 38
===============================================================================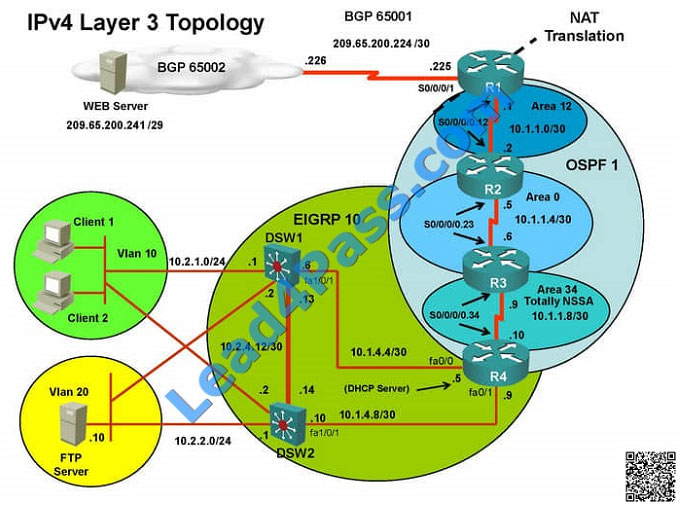
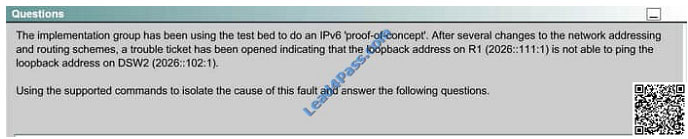 The implementation group has been using the test bed to do an IPv6 \\’proof-of-concept1.
The implementation group has been using the test bed to do an IPv6 \\’proof-of-concept1.
After several changes to the network addressing and routing schemes, a trouble ticket has been opened indicating that
the loopback address on R1 (2026::111:1) is not able to ping the loopback address on DSW2 (2026::102:1).
Use the supported commands to isolate the cause of this fault and answer the following question.
What is the solution to the fault condition?
A. Under the interface Tunnel34 configuration enter the ipv6 ospf 6 area 34 command.
B. Under the interface Loopback6 configuration enter the ipv6 ospf 6 area 34 command.
C. Under the interface Serial0/0/0.34 configuration enter the ipv6 ospf 6 area 34 command.
D. Under ipv6 router ospf 6 configuration enter the redistribute rip RIP_ZONE includeconnected command.
Correct Answer: D
As explained earlier, the problem is with route redistribution on R4 of not redistributing RIP routes into OSPF for IPV6.
QUESTION 39
Choose and place in the right order headers when monitoring GRE packet:
Select and Place: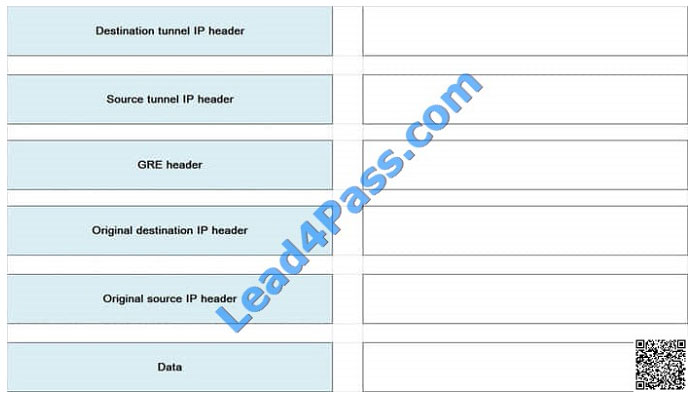
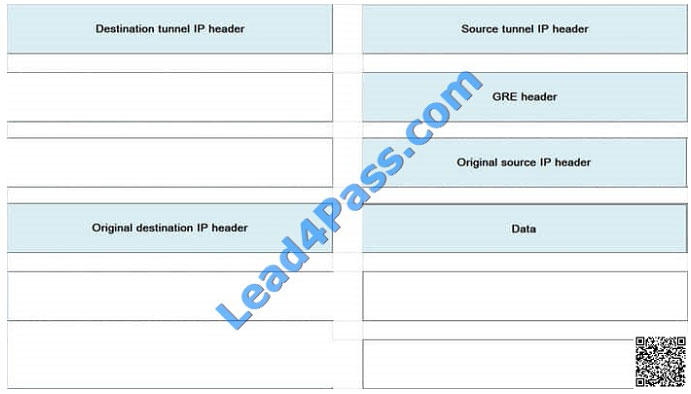
QUESTION 40
Which IPsec mode will encrypt a GRE tunnel to provide multiprotocol support and reduced overhead?
A. 3DES
B. multipoint GRE
C. tunnel
D. transport
Correct Answer: D
We offer more ways to make it easier for everyone to learn, and YouTube is the best tool in the video.
Follow channels: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCXg-xz6fddo6wo1Or9eHdIQ/videos get more useful exam content.
Latest Cisco 300-135 YouTube videos:
This is the latest update released by the Cisco CCNP Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOTv2) 300-135 exam questions and answers, and we share 40 exam questions and answers for free to help you improve your skills! You can download 300-135 pdf or watch the 300-135 YouTube video tutorial online! Get the full 300-135 exam dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-135.html (Total questions:308 Q&A). Help you pass the exam quickly!
[PDF] Free Cisco 300-135 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1t2DGWCrKH4lUzDTYYVUjacRNffholtDK
[PDF] Free Full Cisco pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1CMo2G21nPLf7ZmI-3_hBpr4GDKRQWrGx
leads4pass Promo Code 12% Off

We share more practical and effective exam dumps
(Cisco,Microsoft,Oracle,Citrix,Comptia…) The latest microsoft mcsa windows 70-697 exam dumps help you improve your skills